Variables and Aliases
What you'll learn
- How to deal with async commands
- What Aliases are and how they simplify your code
- Why you rarely need to use variables with Cypress
- How to use Aliases for objects, elements and routes
Return Values
New users to Cypress may initially find it challenging to work with the asynchronous nature of our APIs.
Do not worry!
There are many ways to reference, compare and utilize the objects that Cypress commands yield you.
Once you get the hang of async code you'll realize you can do everything you could do synchronously, without your code doing any backflips.
This guide explores many common patterns for writing good Cypress code that can handle even the most complex situations.
Asynchronous APIs are here to stay in JavaScript. They are found everywhere in modern code. In fact, most new browser APIs are asynchronous and many core Node modules are asynchronous as well.
The patterns we'll explore below are useful in and outside of Cypress.
The first and most important concept you should recognize is...
Return Values
You cannot assign or work with the return values of any Cypress command. Commands are enqueued and run asynchronously.
// this won't work the way you think it does
const button = cy.get('button')
const form = cy.get('form')
button.click()
Closures
To access what each Cypress command yields you use
.then().
cy.get('button').then(($btn) => {
// $btn is the object that the previous
// command yielded us
})
If you're familiar with
native Promises
the Cypress .then() works the same way. You can continue to nest more Cypress
commands inside of the .then().
Each nested command has access to the work done in previous commands. This ends up reading very nicely.
cy.get('button').then(($btn) => {
// store the button's text
const txt = $btn.text()
// submit a form
cy.get('form').submit()
// compare the two buttons' text
// and make sure they are different
cy.get('button').should(($btn2) => {
expect($btn2.text()).not.to.eq(txt)
})
})
// these commands run after all of the
// other previous commands have finished
cy.get(...).find(...).should(...)
The commands outside of the .then() will not run until all of the nested
commands finish.
By using callback functions we've created a closure. Closures enable us to keep references around to refer to work done in previous commands.
Debugging
Using .then() functions is an excellent opportunity to use
debugger.
This can help you understand the order in which commands are run. This also
enables you to inspect the objects that Cypress yields you in each command.
cy.get('button').then(($btn) => {
// inspect $btn <object>
debugger
cy.get('[data-testid="countries"]')
.select('USA')
.then(($select) => {
// inspect $select <object>
debugger
cy.clock().then(($clock) => {
// inspect $clock <object>
debugger
$btn // is still available
$select // is still available too
})
})
})
Variables
Typically in Cypress you hardly need to ever use const, let, or var. When
using closures you'll always have access to the objects that were yielded to you
without assigning them.
The one exception to this rule is when you are dealing with mutable objects (that change state). When things change state you often want to compare an object's previous value to the next value.
Here's a great use case for a const.
<button>increment</button>
you clicked button <span data-testid="num">0</span> times
// app code
let count = 0
$('button').on('click', () => {
$('[data-testid="num"]').text((count += 1))
})
// cypress test code
cy.get('[data-testid="num"]').then(($span) => {
// capture what num is right now
const num1 = parseFloat($span.text())
cy.get('button')
.click()
.then(() => {
// now capture it again
const num2 = parseFloat($span.text())
// make sure it's what we expected
expect(num2).to.eq(num1 + 1)
})
})
The reason for using const is because the $span object is mutable. Whenever
you have mutable objects and you're trying to compare them, you'll need to store
their values. Using const is a perfect way to do that.
Aliases
Using .then() callback functions to access the previous command values is
great—but what happens when you're running code in hooks like before or
beforeEach?
beforeEach(() => {
cy.get('button').then(($btn) => {
const text = $btn.text()
})
})
it('does not have access to text', () => {
// how do we get access to text ?!?!
})
How will we get access to text?
We could make our code do some ugly backflips using let to get access to it.
Do not do this
This code below is just for demonstration.
describe('a suite', () => {
// this creates a closure around
// 'text' so we can access it
let text
beforeEach(() => {
cy.get('button').then(($btn) => {
// redefine text reference
text = $btn.text()
})
})
it('does have access to text', () => {
// now text is available to us
// but this is not a great solution :(
text
})
})
Fortunately, you don't have to make your code do backflips. With Cypress, we can better handle these situations.
Introducing Aliases
Aliases are a powerful construct in Cypress that have many uses. We'll explore each of their capabilities below.
At first, we'll use them to share objects between your hooks and your tests.
Sharing Context
Sharing context is the simplest way to use aliases.
To alias something you'd like to share use the .as()
command.
Let's look at our previous example with aliases.
beforeEach(() => {
// alias the $btn.text() as 'text'
cy.get('button').invoke('text').as('text')
})
it('has access to text', function () {
this.text // is now available
})
Under the hood, aliasing basic objects and primitives utilizes Mocha's shared
context object:
that is, aliases are available as this.*.
Mocha automatically shares contexts for us across all applicable hooks for each test. Additionally these aliases and properties are automatically cleaned up after each test.
describe('parent', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
cy.wrap('one').as('a')
})
context('child', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
cy.wrap('two').as('b')
})
describe('grandchild', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
cy.wrap('three').as('c')
})
it('can access all aliases as properties', function () {
expect(this.a).to.eq('one') // true
expect(this.b).to.eq('two') // true
expect(this.c).to.eq('three') // true
})
})
})
})
Accessing Fixtures:
The most common use case for sharing context is when dealing with
cy.fixture().
Often times you may load a fixture in a beforeEach hook but want to utilize
the values in your tests.
beforeEach(() => {
// alias the users fixtures
cy.fixture('users.json').as('users')
})
it('utilize users in some way', function () {
// access the users property
const user = this.users[0]
// make sure the header contains the first
// user's name
cy.get('header').should('contain', user.name)
})
Watch out for async commands
Do not forget that Cypress commands are async!
You cannot use a this.* reference until the .as() command runs.
it('is not using aliases correctly', function () {
cy.fixture('users.json').as('users')
// nope this won't work
//
// this.users is not defined
// because the 'as' command has only
// been enqueued - it has not run yet
const user = this.users[0]
})
The same principles we introduced many times before apply to this situation. If
you want to access what a command yields you have to do it in a closure using a
.then().
// yup all good
cy.fixture('users.json').then((users) => {
// now we can avoid the alias altogether
// and use a callback function
const user = users[0]
// passes
cy.get('header').should('contain', user.name)
})
Avoiding the use of this
Arrow Functions
Accessing aliases as properties with this.* will not work if you use
arrow functions
for your tests or hooks.
This is why all of our examples use the regular function () {} syntax as
opposed to the lambda "fat arrow" syntax () => {}.
Instead of using the this.* syntax, there is another way to access aliases.
The cy.get() command is capable of accessing aliases with
a special syntax using the @ character:
beforeEach(() => {
// alias the users fixtures
cy.fixture('users.json').as('users')
})
it('utilize users in some way', function () {
// use the special '@' syntax to access aliases
// which avoids the use of 'this'
cy.get('@users').then((users) => {
// access the users argument
const user = users[0]
// make sure the header contains the first
// user's name
cy.get('header').should('contain', user.name)
})
})
By using cy.get() we avoid the use of this.
Keep in mind that there are use cases for both approaches because they have different ergonomics.
When using this.users we have access to it synchronously, whereas when using
cy.get('@users') it becomes an asynchronous command.
You can think of the cy.get('@users') as doing the same thing as
cy.wrap(this.users).
Elements
Aliases have other special characteristics when being used with DOM elements.
After you alias DOM elements, you can then later access them for reuse.
// alias all of the tr's found in the table as 'rows'
cy.get('table').find('tr').as('rows')
Internally, Cypress has made a reference to the <tr> collection returned as
the alias "rows". To reference these same "rows" later, you can use the
cy.get() command.
// Cypress returns the reference to the <tr>'s
// which allows us to continue to chain commands
// finding the 1st row.
cy.get('@rows').first().click()
Because we've used the @ character in cy.get(), instead
of querying the DOM for elements, cy.get() looks for an
existing alias called rows and returns the reference (if it finds it).
Stale Elements:
In many single-page JavaScript applications the DOM re-renders parts of the
application constantly. If you alias DOM elements that have been removed from
the DOM by the time you call cy.get() with the alias,
Cypress automatically re-queries the DOM to find these elements again.
<ul id="todos">
<li>
Walk the dog
<button class="edit">edit</button>
</li>
<li>
Feed the cat
<button class="edit">edit</button>
</li>
</ul>
Let's imagine when we click the .edit button that our <li> is re-rendered in
the DOM. Instead of displaying the edit button it instead displays an
<input /> text field allowing you to edit the todo. The previous <li> has
been completely removed from the DOM and a new <li> is rendered in its
place.
cy.get('[data-testid="todos"] li').first().as('firstTodo')
cy.get('@firstTodo').find('.edit').click()
cy.get('@firstTodo')
.should('have.class', 'editing')
.find('input')
.type('Clean the kitchen')
When we reference @firstTodo, Cypress checks to see if all of the elements it
is referencing are still in the DOM. If they are, it returns those existing
elements. If they aren't, Cypress replays the commands leading up to the alias
definition.
In our case it would re-issue the commands: cy.get('#todos li').first().
Everything works because the new <li> is found.
Usually, replaying previous commands will return what you expect, but not always. It is recommended that you alias elements as soon as possible instead of further down a chain of commands.
cy.get('nav header [data-testid="user"]').as('user')(good)cy.get('nav').find('header').find('[data-testid="user"]').as('user')(bad)
When in doubt, you can always issue a regular cy.get()
to query for the elements again.
Intercepts
Aliases can also be used with cy.intercept(). Aliasing your intercepted routes enables you to:
- ensure your application makes the intended requests
- wait for your server to send the response
- access the actual request object for assertions
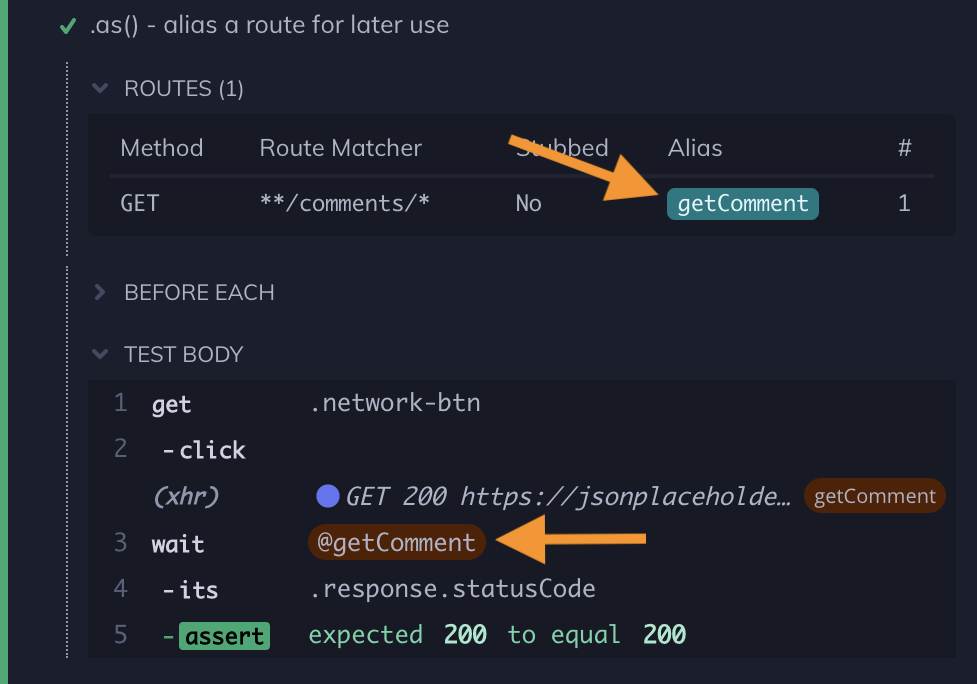
Here's an example of aliasing an intercepted route and waiting on it to complete.
cy.intercept('POST', '/users', { id: 123 }).as('postUser')
cy.get('form').submit()
cy.wait('@postUser').then(({ request }) => {
expect(request.body).to.have.property('name', 'Brian')
})
cy.contains('Successfully created user: Brian')
Requests
Aliases can also be used with requests.
Here's an example of aliasing a request and accessing its properties later.
cy.request('https://jsonplaceholder.cypress.io/comments').as('comments')
// other test code here
cy.get('@comments').should((response) => {
if (response.status === 200) {
expect(response).to.have.property('duration')
} else {
// whatever you want to check here
}
})
})
Aliases are reset before each test
Note: all aliases are reset before each test. A common user mistake is to
create aliases using the before hook. Such aliases work in the first test
only!
// 🚨 THIS EXAMPLE DOES NOT WORK
before(() => {
// notice this alias is created just once using "before" hook
cy.wrap('some value').as('exampleValue')
})
it('works in the first test', () => {
cy.get('@exampleValue').should('equal', 'some value')
})
// NOTE the second test is failing because the alias is reset
it('does not exist in the second test', () => {
// there is not alias because it is created once before
// the first test, and is reset before the second test
cy.get('@exampleValue').should('equal', 'some value')
})
The solution is to create the aliases before each test using the beforeEach
hook
// ✅ THE CORRECT EXAMPLE
beforeEach(() => {
// we will create a new alias before each test
cy.wrap('some value').as('exampleValue')
})
it('works in the first test', () => {
cy.get('@exampleValue').should('equal', 'some value')
})
it('works in the second test', () => {
cy.get('@exampleValue').should('equal', 'some value')
})
See also
- Blog: Load Fixtures from Cypress Custom Commands explains how to load or import fixtures to be used in the Cypress custom commands.