contains
Get the DOM element containing the text. DOM elements can contain more than the desired text and still match. Additionally, Cypress prefers some DOM elements over the deepest element found.
Syntax
.contains(content)
.contains(content, options)
.contains(selector, content)
.contains(selector, content, options)
// ---or---
cy.contains(content)
cy.contains(content, options)
cy.contains(selector, content)
cy.contains(selector, content, options)
Usage
Correct Usage
cy.get('.nav').contains('About') // Yield el in .nav containing 'About'
cy.contains('Hello') // Yield first el in document containing 'Hello'
Incorrect Usage
cy.title().contains('My App') // Errors, 'title' does not yield DOM element
cy.getCookies().contains('_key') // Errors, 'getCookies' does not yield DOM element
Arguments
content (String, Number, RegExp)
Get the DOM element containing the content.
selector (String selector)
Specify a selector to filter DOM elements containing the text. Cypress will ignore its default preference order for the specified selector. Using a selector allows you to return more shallow elements (higher in the tree) that contain the specific text.
options (Object)
Pass in an options object to change the default behavior of .contains().
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
matchCase | true | Check case sensitivity |
log | true | Displays the command in the Command log |
timeout | defaultCommandTimeout | Time to wait for .contains() to resolve before timing out |
includeShadowDom | includeShadowDom config option value | Whether to traverse shadow DOM boundaries and include elements within the shadow DOM in the yielded results. |
Yields
-
.contains()yields the new DOM element it found.
Examples
Content
Find the first element containing some text
<ul>
<li>apples</li>
<li>oranges</li>
<li>bananas</li>
</ul>
// yields <li>apples</li>
cy.contains('apples')
Find the input[type='submit'] by value
Get the form element and search in its descendants for the content "submit the form!"
<div id="main">
<form>
<div>
<label>name</label>
<input name="name" />
</div>
<div>
<label>age</label>
<input name="age" />
</div>
<input type="submit" value="submit the form!" />
</form>
</div>
// yields input[type='submit'] element then clicks it
cy.get('form').contains('submit the form!').click()
Number
Find the first element containing a number
Even though the <span> is the deepest element that contains a "4", Cypress
automatically yields <button> elements over spans because of its
preferred element order.
<button class="btn btn-primary" type="button">
Messages <span class="badge">4</span>
</button>
// yields <button>
cy.contains(4)
Regular Expression
Find the first element with text matching the regular expression
<ul>
<li>apples</li>
<li>oranges</li>
<li>bananas</li>
</ul>
// yields <li>bananas</li>
cy.contains(/^b\w+/)
Selector
Specify a selector to return a specific element
Technically the <html>, <body>, <ul>, and first <li> in the example
below all contain "apples".
Normally Cypress would return the first <li> since that is the deepest
element that contains "apples".
To override the element that is yielded we can pass 'ul' as the selector.
<html>
<body>
<ul>
<li>apples</li>
<li>oranges</li>
<li>bananas</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
// yields <ul>...</ul>
cy.contains('ul', 'apples')
Keep the form as the subject
Here's an example that uses the selector to ensure that the <form> remains the
subject for
future chaining.
<form>
<div>
<label>name</label>
<input name="name" />
</div>
<button type="submit">Proceed</button>
</form>
cy.get('form') // yields <form>...</form>
.contains('form', 'Proceed') // yields <form>...</form>
.submit() // yields <form>...</form>
Without the explicit selector the subject would change to be the <button>.
Using the explicit selector ensures that chained commands will have the <form>
as the subject.
Case Sensitivity
Here's an example using the matchCase option to ignore case sensitivity.
<div>Capital Sentence</div>
cy.get('div').contains('capital sentence') // fail
cy.get('div').contains('capital sentence', { matchCase: false }) // pass
Notes
Scopes
.contains() acts differently whether it's starting a series of commands or
being chained off an existing series.
When starting a series of commands:
This queries the entire document for the content.
cy.contains('Log In')
When chained to an existing series of commands
This will query inside of the <#checkout-container> element.
cy.get('#checkout-container').contains('Buy Now')
Be wary of chaining multiple contains
Let's imagine a scenario where you click a button to delete a user and a dialog appears asking you to confirm this deletion.
// This doesn't work as intended
cy.contains('Delete User').click().contains('Yes, Delete!').click()
Because the second .contains() is chained off of a command that yielded the
<button>, Cypress will look inside of the <button> for the new content.
In other words, Cypress will look inside of the <button> containing "Delete
User" for the content: "Yes, Delete!", which is not what we intended.
What you want to do is call cy again, which automatically creates a new chain
scoped to the document.
cy.contains('Delete User').click()
cy.contains('Yes, Delete!').click()
Leading, trailing, duplicate whitespaces aren't ignored in <pre> tag
Unlike other tags, <pre> doesn't ignore leading, trailing, or duplicate
whitespaces as shown below:
<!--Code for test-->
<h2>Other tags</h2>
<p>Hello, World !</p>
<h2>Pre tag</h2>
<pre> Hello, World !</pre>
Rendered result:

To reflect this behavior, Cypress also doesn't ignore them.
// test result for above code
cy.get('p').contains('Hello, World !') // pass
cy.get('p').contains(' Hello, World !') // fail
cy.get('pre').contains('Hello, World !') // fail
cy.get('pre').contains(' Hello, World !') // pass
Non-breaking space
You can use a space character in cy.contains() to match text in the HTML that
uses a non-breaking space entity .
<span>Hello world</span>
// finds the span element
cy.contains('Hello world')
Tip: read about assertions against a text with non-breaking space entities in How do I get an element's text contents?
Single Element
Only the first matched element will be returned
<ul id="header">
<li>Welcome, Jane Lane</li>
</ul>
<div id="main">
<span>These users have 10 connections with Jane Lane</span>
<ul>
<li>Jamal</li>
<li>Patricia</li>
</ul>
</div>
The below example will return the <li> in the #header since that is the
first element that contains the text "Jane Lane".
// yields #header li
cy.contains('Jane Lane')
If you wanted to select the <span> instead, you could narrow the elements
yielded before the .contains().
// yields <span>
cy.get('#main').contains('Jane Lane')
Default <input type="submit"> labels
When the value attribute is omitted from an <input type="submit">, the
default label is used and can be locale-dependent.
More info at MDN.
When this happens, the value is an empty string, and there is no programmatic
way for Cypress to filter elements by the label displayed by the user agent.
This can cause unexpected failures when using cy.contains() with submit
buttons.
The solution in this case is to:
// assert the empty string
cy.get('input').should('have.value', '')
// ---or---
// if possible, set the `value` attribute
<input type=submit value="Submit" />
Preferences
Element preference order
.contains() defaults to preferring elements higher in the tree when they are:
input[type='submit']buttonalabel
Cypress will ignore this element preference order if you pass a selector
argument to .contains().
Favor of <button> over other deeper elements
Even though the <span> is the deepest element that contains "Search", Cypress
yields <button> elements over spans.
<form>
<button>
<i class="fa fa-search"></i>
<span>Search</span>
</button>
</form>
// yields <button>
cy.contains('Search').children('i').should('have.class', 'fa-search')
Favor of <a> over other deeper elements
Even though the <span> is the deepest element that contains "Sign Out",
Cypress yields anchor elements over spans.
<nav>
<a href="/users">
<span>Users</span>
</a>
<a href="/signout">
<span>Sign Out</span>
</a>
</nav>
// yields <a>
cy.get('nav').contains('Sign Out').should('have.attr', 'href', '/signout')
Favor of <label> over other deeper elements
Even though the <span> is the deepest element that contains "Age", Cypress
yields <label> elements over <span>.
<form>
<label>
<span>Name:</span>
<input name="name" />
</label>
<label>
<span>Age:</span>
<input name="age" />
</label>
</form>
// yields label
cy.contains('Age').find('input').type('29')
Rules
Requirements
-
.contains()can be chained off ofcyor off a command that yields DOM element(s).
Assertions
-
.contains()will automatically retry until the element(s) exist in the DOM -
.contains()will automatically retry until all chained assertions have passed
Timeouts
-
.contains()can time out waiting for the element(s) to exist in the DOM . -
.contains()can time out waiting for assertions you've added to pass.
Command Log
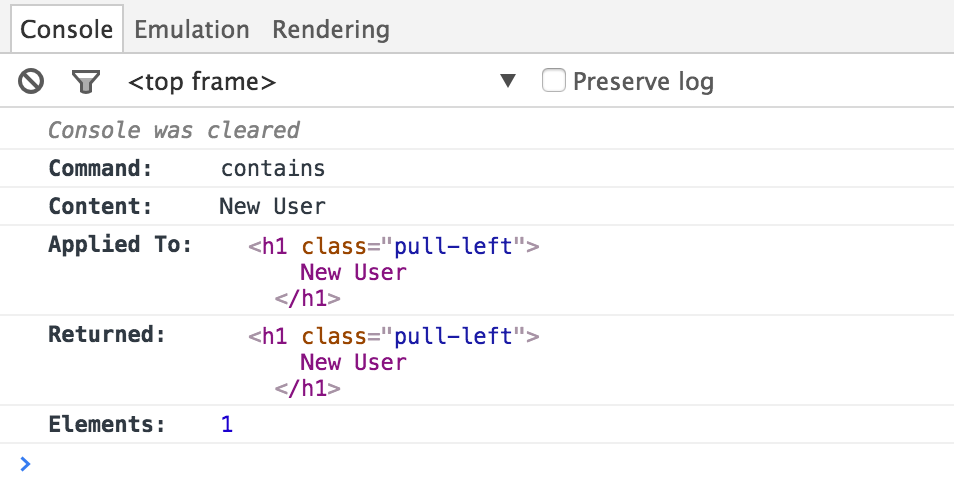
Element contains text "New User"
cy.get('h1').contains('New User')
The commands above will display in the Command Log as:

When clicking on the contains command within the command log, the console
outputs the following:
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| 5.2.0 | Added includeShadowDom option. |
| 4.0.0 | Added support for option matchCase. |